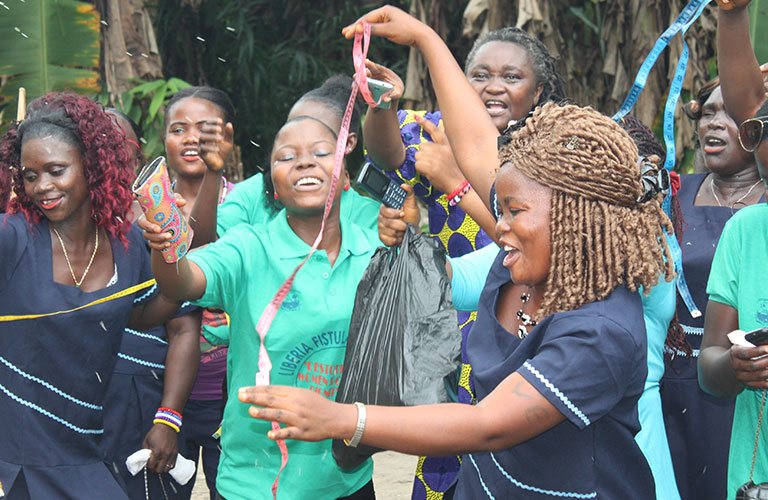I have
the power
to change
my world
UNFPA Annual Report 2017
17709
Year on year, millions of women and adolescents in 155 countries and territories have been progressively able to exercise their sexual and reproductive health and rights. This is in no small measure as a result of UNFPA programmes and activities.
The UNFPA strategic plan for 2014-2017 set ambitious targets for increasing access to sexual and reproductive health services. These services have empowered millions of women to make their own decisions about whether, when or how often to become pregnant. They have enabled millions of teenagers to avoid unplanned pregnancy, and to make safe and healthy transitions to adulthood. And they have slowed the unnecessary and cruel tide of maternal death.
Access to safe, voluntary family planning is a human right and is central to achieving gender equality, empowering women and reducing poverty. UNFPA helps ensure steady supplies of high-quality contraceptives.
2017
2014-2017
Affordable, high-quality reproductive health services save lives. Maternal deaths are decreasing rapidly in developing countries, particularly in the least-developed ones and in countries of East and Southern Africa. Between 2014 and 2017, UNFPA-supported integrated sexual and reproductive health services, including skilled birth attendance, reached more than 58 million people.
2017
2014-2017
UNFPA programmes enabled millions of adolescents and young people to access sexual and reproductive health services. UNFPA has also advocated the elimination of harmful practices, such as child marriage and female genital mutilation.
2017
2014-2017
Services supported by UNFPA reached millions of women and young people in East and Southern Africa between 2014 and 2017. In 2017 alone through a programme funded by the United Kingdom to prevent maternal deaths in the region, UNFPA helped 3.4 million people access family planning and trained about 6,000 health workers to provide a wider range of contraceptive options and information about their safe use.
UNFPA in 2017 also invested in integrated HIV and sexual and reproductive health services in Southern Africa, which has the world’s highest HIV infection rates. In the Great Lakes region and in other crisis affected areas, UNFPA provided maternal health care and support for survivors of gender-based violence. Also, UNFPA is supporting comprehensive sexuality education programmes in all countries in the region.

Programme Expenses
In millions of US$
(includes core and non-core resources)
Angola
2017: 2.5
2014-2017: 9.8
Botswana
2017: 0.9
2014-2017: 5.0
Burundi
2017: 5.7
2014-2017: 23.2
Comoros
2017: 0.9
2014-2017: 3.9
Democratic Republic of the Congo
2017: 19.4
2014-2017: 74.9
Eritrea
2017: 1.9
2014-2017: 8.7
Ethiopia
2017: 13.7
2014-2017: 61.8
Kenya
2017: 9.3
2014-2017: 42.0
Lesotho
2017: 1.5
2014-2017: 7.3
Madagascar
2017: 5.6
2014-2017: 22.8
Malawi
2017: 4.4
2014-2017: 33.9
Mauritius
2017: 0.1
2014-2017: 0.4
Mozambique
2017: 16.6
2014-2017: 46.1
Namibia
2017: 1.0
2014-2017: 5.5
Rwanda
2017: 3.1
2014-2017: 16.3
South Africa
2017: 1.7
2014-2017: 9.7
South Sudan
2017: 20.3
2014-2017: 75.6
Eswatini
2017: 1.4
2014-2017: 6.6
Uganda
2017: 12.9
2014-2017: 67.0
United Republic of Tanzania
2017: 11.4
2014-2017: 48.4
Zambia
2017: 8.7
2014-2017: 31.6
Zimbabwe
2017: 14.4
2014-2017: 70.2
Country/territory activities
2017: 157.4
2014-2017: 670.7
Regional activities
2017: 18.9
2014-2017: 53.0
Total programme expenses
2017: 176.3
2014-2017: 723.7
Programme expenses by purpose
In millions of US$
UNFPA empowered the region’s women and young people between 2014 and 2017 through improved sexual and reproductive health services and increased access to family planning. Investments strengthened countries’ capacities to provide and distribute reproductive health supplies. In 2016, for example, UNFPA invested about $33 million in contraceptives.
UNFPA also invested in developing the region’s biggest asset: its young people. These investments supported initiatives to foster youth participation, with partners such as the African Youth and Adolescent Network on Population and Development, in policymaking and development planning, and to create synergies among UNFPA programmes. Efforts are also under way to realize and maximize a demographic dividend by scaling up investments in the human capital of the region’s young people.

Programme Expenses
In millions of US$
(includes core and non-core resources)
Benin
2017: 3.0
2014-2017: 15.3
Burkina Faso
2017: 7.0
2014-2017: 31.3
Cameroon
2017: 5.5
2014-2017: 25.7
Cape Verde
2017: 0.5
2014-2017: 3.3
Central African Republic
2017: 3.3
2014-2017: 16.3
Chad
2017: 6.0
2014-2017: 24.7
Congo
2017: 2.2
2014-2017: 10.9
Côte d'Ivoire
2017: 6.7
2014-2017: 32.8
Equatorial Guinea
2017: 1.7
2014-2017: 6.0
Gabon
2017: 0.6
2014-2017: 3.3
Gambia
2017: 1.5
2014-2017: 6.7
Ghana
2017: 3.1
2014-2017: 15.9
Guinea
2017: 5.9
2014-2017: 30.5
Guinea-Bissau
2017: 1.7
2014-2017: 8.2
Liberia
2017: 7.1
2014-2017: 31.7
Mali
2017: 5.5
2014-2017: 18.6
Mauritania
2017: 2.3
2014-2017: 11.3
Niger
2017: 12.3
2014-2017: 47.9
Nigeria
2017: 19.1
2014-2017: 97.5
São Tomé and Príncipe
2017: 0.7
2014-2017: 4.3
Senegal
2017: 3.8
2014-2017: 22.6
Sierra Leone
2017: 21.8
2014-2017: 64.9
Togo
2017: 2.3
2014-2017: 14.3
Country/territory activities
2017: 123.6
2014-2017: 544.0
Regional activities
2017: 9.0
2014-2017: 31.2
Total programme expenses
2017: 132.6
2014-2017: 575.2
Programme expenses by purpose
In millions of US$
Between 2014 and 2017, UNFPA advocated integrating sexual and reproductive health into national health policies and systems with an emphasis on strengthening services that prevent maternal deaths. It also advocated for the inclusion of reproductive rights in governments’ human rights policies.
UNFPA programmes in the Arab States engaged governments, community leaders and civil society organizations in efforts to end harmful practices such as child marriage and female genital mutilation. Using data collected through focus groups and other means, UNFPA also responded to women’s and girls’ needs for sexual and reproductive health services and services to address gender-based violence. Regional programmes have sought to reinforce the role of young men and women in policymaking and engage them in promoting peace and security.

Programme Expenses
In millions of US$
(includes core and non-core resources)
Algeria
2017: 0.2
2014-2017: 1.6
Djibouti
2017: 0.8
2014-2017: 4.4
Egypt
2017: 3.4
2014-2017: 15.6
Iraq
2017: 50.0
2014-2017: 97.6
Jordan
2017: 15.6
2014-2017: 45.1
Lebanon
2017: 6.6
2014-2017: 16.8
Libya
2017: 2.0
2014-2017: 4.8
Morocco
2017: 1.0
2014-2017: 5.1
Oman
2017: 0.9
2014-2017: 3.9
Palestine
2017: 3.8
2014-2017: 11.4
Somalia
2017: 11.8
2014-2017: 61.0
Sudan
2017: 13.9
2014-2017: 56.7
Syrian Arab Republic
2017: 18.3
2014-2017: 51.3
Tunisia
2017: 1.3
2014-2017: 3.7
Yemen
2017: 9.7
2014-2017: 36.1
Country/territory activities
2017: 139.3
2014-2017: 415.1
Regional activities
2017: 5.0
2014-2017: 26.7
Total programme expenses
2017: 144.3
2014-2017: 441.8
Programme expenses by purpose
In millions of US$
UNFPA programmes in Asia and the Pacific between 2014 and 2017 helped reduce maternal deaths, address unmet need for family planning and tackle gender-based violence and harmful practices against women and girls.
As part of these efforts, UNFPA supported the training of midwives who have been deployed to underserved areas of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Myanmar, Mongolia and Nepal, resulting in a dramatic reduction in maternal deaths.
Advocacy contributed to increased access to family planning and strengthened responses to child marriage. Services in humanitarian settings helped meet the sexual and reproductive health needs of vulnerable women and girls and address gender-based violence.

Programme Expenses
In millions of US$
(includes core and non-core resources)
Afghanistan
2017: 12.7
2014-2017: 78.3
Bangladesh
2017: 13.4
2014-2017: 49.5
Bhutan
2017: 0.5
2014-2017: 3.3
Cambodia
2017: 2.0
2014-2017: 14.3
China
2017: 2.2
2014-2017: 12.2
Democratic People's Republic of Korea
2017: 1.8
2014-2017: 7.4
India
2017: 6.3
2014-2017: 35.7
Indonesia
2017: 4.8
2014-2017: 17.6
Iran (Islamic Republic of)
2017: 1.3
2014-2017: 5.6
Lao People's Democratic Republic
2017: 2.1
2014-2017: 11.9
Malaysia
2017: 0.7
2014-2017: 2.9
Maldives
2017: 0.2
2014-2017: 1.7
Mongolia
2017: 3.0
2014-2017: 14.8
Myanmar
2017: 13.3
2014-2017: 70.1
Nepal
2017: 5.9
2014-2017: 25.0
Pacific Multi Islands *
2017: 3.9
2014-2017: 22.6
Pakistan
2017: 6.0
2014-2017: 30.9
Papua New Guinea
2017: 3.4
2014-2017: 14.2
Philippines
2017: 3.7
2014-2017: 29.3
Sri Lanka
2017: 0.9
2014-2017: 4.8
Thailand
2017: 0.8
2014-2017: 5.0
Timor-Leste
2017: 1.9
2014-2017: 8.1
Viet Nam
2017: 2.1
2014-2017: 15.5
Country/territory activities
2017: 92.9
2014-2017: 480.7
Regional activities
2017: 7.6
2014-2017: 30.4
Total programme expenses
2017: 100.5
2014-2017: 511.1
* Figures for Pacific multi-islands comprise several islands which, for reporting purposes, are classified under one heading, including the Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, the Federated States of Micronesia, Nauru, Niue, Palau, Samoa, the Solomon Islands, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu and Vanuatu.
Programme expenses by purpose
In millions of US$
In Eastern Europe and Central Asia, a region of middle-income countries, UNFPA helped governments develop or implement policies to ensure that all people, including the most vulnerable, can realize their right to sexual and reproductive health.
Other actions in the region helped break down barriers that young people face in accessing sexual and reproductive health information and services, supported national efforts to eradicate gender-based violence and harmful practices and strengthened national capacities for collecting, analysing and using data for policymaking.
Programme Expenses
In millions of US$
(includes core and non-core resources)
Albania
2017: 1.2
2014-2017: 3.7
Armenia
2017: 0.6
2014-2017: 2.9
Azerbaijan
2017: 0.8
2014-2017: 2.6
Belarus
2017: 1.1
2014-2017: 3.2
Bosnia and Herzegovina
2017: 0.6
2014-2017: 3.2
Georgia
2017: 1.3
2014-2017: 6.0
Kazakhstan
2017: 0.6
2014-2017: 3.0
Kyrgyzstan
2017: 0.9
2014-2017: 4.9
Republic of Moldova
2017: 0.7
2014-2017: 3.2
Serbia *
2017: 1.1
2014-2017: 4.3
Tajikistan
2017: 2.0
2014-2017: 6.7
North Macedonia
2017: 0.3
2014-2017: 1.4
Türki̇ye
2017: 22.1
2014-2017: 39.4
Turkmenistan
2017: 0.6
2014-2017: 2.4
Ukraine
2017: 2.8
2014-2017: 8.1
Uzbekistan
2017: 0.8
2014-2017: 4.2
Country/territory activities
2017: 37.5
2014-2017: 99.2
Regional activities
2017: 4.6
2014-2017: 27.6
Total programme expenses
2017: 42.1
2014-2017: 126.8
* Includes Kosovo
Programme expenses by purpose
In millions of US$
UNFPA programmes in Latin America and the Caribbean between 2014 and 2017 helped bolster culturally sensitive, youth-friendly sexual and reproductive health services, ensure reliable reproductive health and family planning supplies, including long-acting reversible contraceptives, for women and young people. Other actions helped extend maternal health services, including midwifery, to indigenous communities and build institutional capacities to address gender-based violence. UNFPA’s evidence-based advocacy influenced policies and strengthened capacities to address gender-based violence and helped reduce child marriage.

Programme Expenses
In millions of US$
(includes core and non-core resources)
Argentina
2017: 0.1
2014-2017: 1.5
Bolivia (Plurinational State of)
2017: 2.7
2014-2017: 11.8
Brazil
2017: 1.4
2014-2017: 6.6
Caribbean, English- and Dutch- speaking *
2017: 1.6
2014-2017: 9.9
Chile
2017: 0.1
2014-2017: 0.8
Colombia
2017: 0.9
2014-2017: 10.5
Costa Rica
2017: 0.4
2014-2017: 2.7
Cuba
2017: 0.7
2014-2017: 3.0
Dominican Republic
2017: 1.2
2014-2017: 3.6
Ecuador
2017: 0.7
2014-2017: 3.7
El Salvador
2017: 1.4
2014-2017: 6.9
Guatemala
2017: 12.8
2014-2017: 28.3
Haiti
2017: 4.4
2014-2017: 19.4
Honduras
2017: 3.2
2014-2017: 13.2
Mexico
2017: 1.4
2014-2017: 5.9
Nicaragua
2017: 0.8
2014-2017: 7.1
Panama
2017: 0.4
2014-2017: 2.9
Paraguay
2017: 0.7
2014-2017: 3.3
Peru
2017: 1.7
2014-2017: 5.8
Uruguay
2017: 1.5
2014-2017: 5.2
Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of)
2017: 0.6
2014-2017: 4.7
Country/territory activities
2017: 38.7
2014-2017: 156.8
Regional activities
2017: 5.0
2014-2017: 28.8
Total programme expenses
2017: 43.7
2014-2017: 185.6
* Figures for Caribbean, English- and Dutch-speaking, comprise several countries and islands which, for reporting purposes, have been classified under one heading, including Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, the British Virgin Islands, the Cayman Islands, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, the Netherlands Antilles (Aruba, Curacao, and St. Maarten), Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago and the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Programme expenses by purpose
In millions of US$
Partnership
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
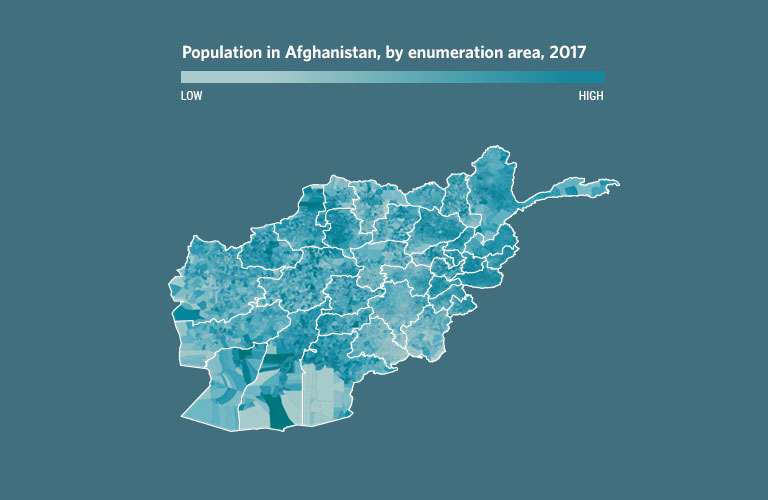
UNFPA partnered with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the United Kingdom Department for International Development and WorldPop/Flowminder to harness the power of spatial reference data to support Afghanistan estimates the in all areas of the country, including those that have been hard to reach because of security concerns.
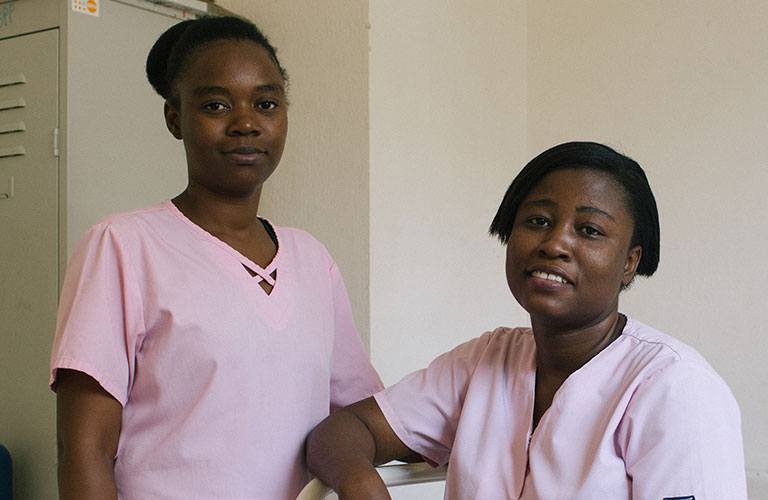


Johnson & Johnson
With support from Johnson & Johnson, UNFPA is helping reduce maternal deaths in Haiti and Liberia by increasing the number and capacity of skilled birth attendants and improving linkages between local communities and maternal health services. At the Marigot maternity clinic, one of five obstetric and newborn care centres supported by Johnson & Johnson in Haiti, midwives provide free maternal health services.
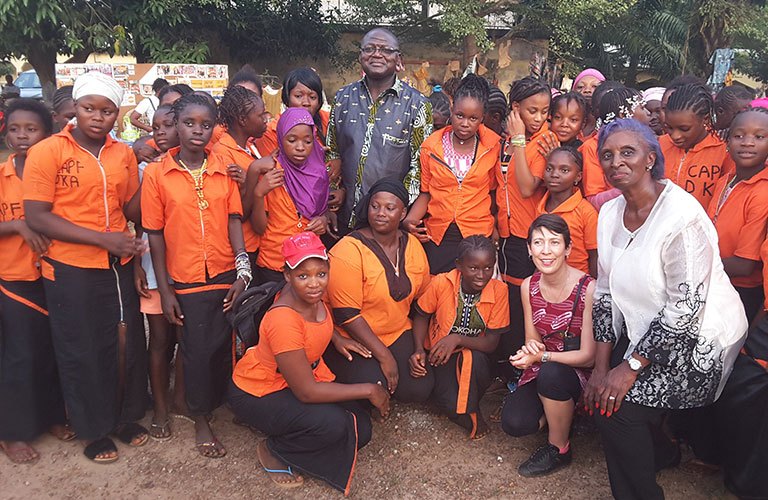


Parliamentarians
Members of Parliament from Africa and Europe see first-hand the impact of maternal health and youth-empowerment programmes in Conakry, Guinea, in 2017.
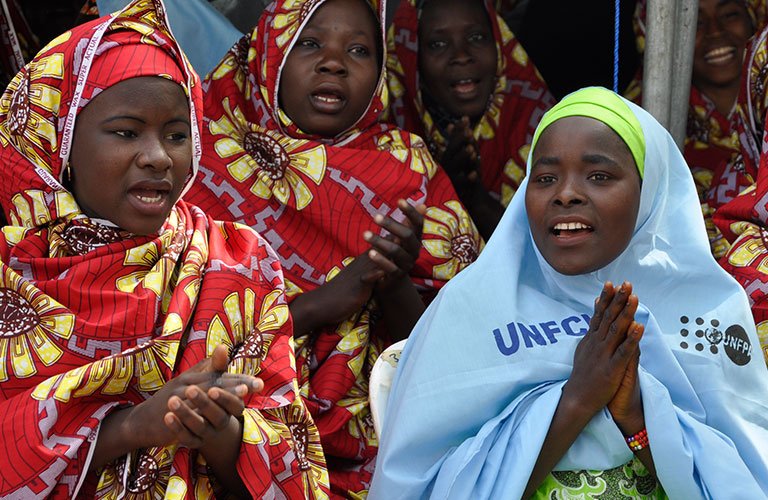


UNFCU Foundation
Healing bodies and minds; transforming lives: With support of the UNFCU Foundation, Fistula Foundation Nigeria and UNFPA enabled 248 women and girls suffering from fistula to be successfully treated in Northern Nigeria. Thirty women were diagnosed with “very complex fistulas” and received access to advanced reconstructive surgical care.

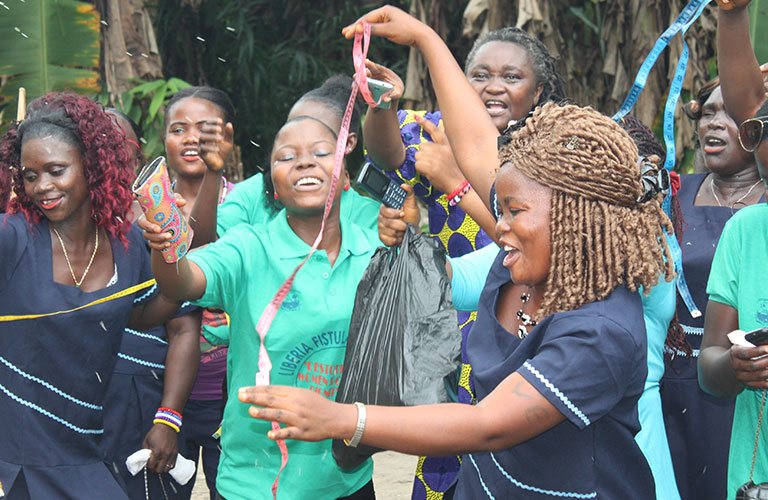
Zonta
Fistula survivors on the day of their graduation from the Liberia Fistula Rehabilitation and Reintegration Centre. The project is delivered by UNFPA with financial support from Zonta International.