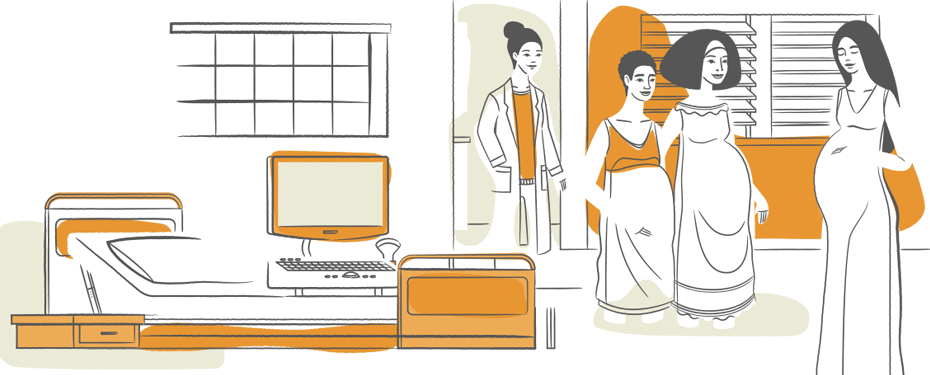
Pregnancy by choice, not by chance


One-hundred seventy-nine governments agreed in 1994 that individuals have the right and should have the means to freely decide whether or when they want to start a family. Yet, an estimated 225 million women in developing countries are unable to exercise that right because they are not using, or have no access to, contraception.
Unmet demand for family planning translates into nearly 60 million unintended pregnancies annually in developing countries.
UNFPA is helping respond to the unmet demand and enabling more women to exercise their right to decide whether, when or how often to become pregnant. Increased access to contraception also leads to fewer abortions and reduces risks to women’s health.
UNFPA provided

male condoms

female condoms

doses of injectable contraceptives

cycles of oral contraceptives
Estimated impact of contraceptives

unintended pregnancies averted

savings in health-care costs